Tally Full form :–
T – Transactions
A – Allowed
L – Linear
L – Line
Y – Yard
Total Accounting Leading List Year
Transactions Allowed in a Linear Line Yard
What are the different versions of Tally?
1. Tally 3.0 (1990) –
Tally 3.0 is the first version of Tally that has been used for the basic accounting needs of small businesses.
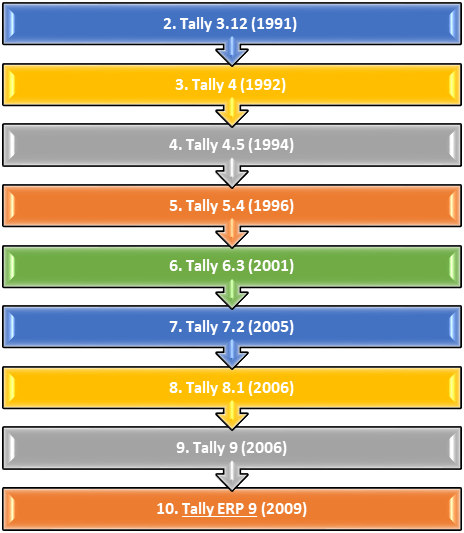
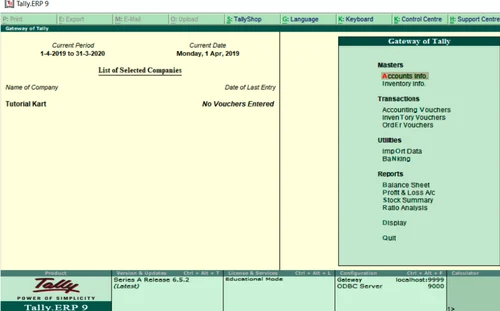
Tally ERP 9 is the latest version of Tally since 2009. There are many business organizations in it. It has advanced features including GST calculations, invoice and payroll processing, remote access, multi-user login and transaction processes. Nowadays, businessmen want a complete business solution software like Tally.
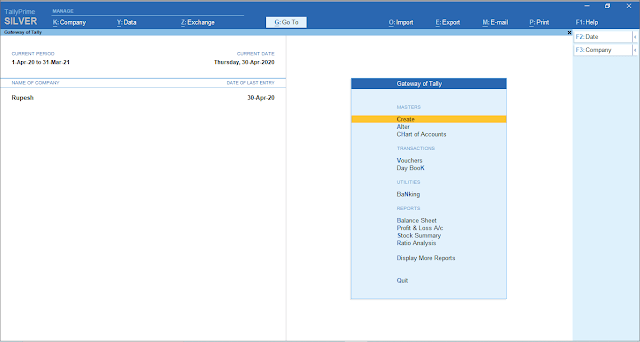
This is the latest version of Tally which has been made advance from tally erp 9 in which we have QR Code, E-invoice, E-Way Bill, Multi Printing, Bank Cancellation update, Oman VAT, e-payment as well as user friendly interface has been prepared.
How to use Tally ?
Tally is accounting in digital format. Maintaining accounts in manual books, we write accounting entries in the form of debits and credits.
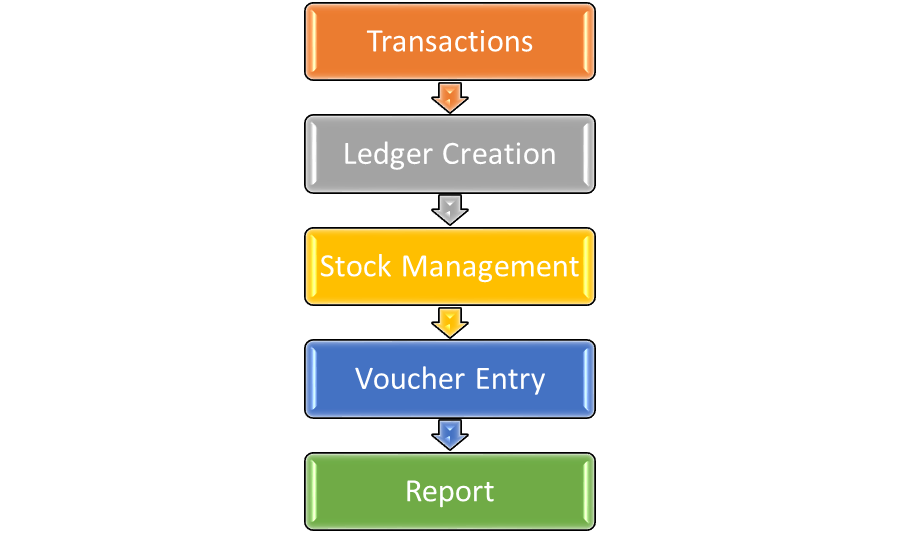
How can we learn tally ?
Basic Accounting Terms:-
Introduction of Accounting: Presently the field of business has expanded considerably. In the changing environment of global economy and business, the complexities of financial transactions have also increased, as a result, accounting has become necessary for a business organization to regulate financial transactions. It is very difficult and impossible to remember every transaction, i.e book-keeping has emerged, Lucas Pacioli is called the father of book-keeping.
In India, the work of determining accounting standards and training of accountants is being done by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India and Institute of Costs and Works Accountants of India.
Meaning and Definition of Book – Keeping:-
It means writing the transactions in books. There are many types of monetary transactions in business which need to be systematically accounted for in the books.
Meaning and Definition of Accounting:-
The work of bookkeeping is only to write the financial transactions in the books of accounts as per the rules, whereas accounting presents the financial results by classifying and summarizing them. To know the economic results, it is necessary for a businessman to collect, classify, summarize and analyze the transactions recorded in the ledger, only then a businessman can conclude the results of his business. This work is completed through accounting.
Objective of Accounting:-
Accounting, as we know that all business transactions are duly recorded in books. Information about all financial transactions related to business and enterprise is obtained through accounting. Its main objectives are as follows –
1. Knowledge of capital
2. Knowledge of buying and selling
3. Knowledge of debtors and creditors
4. Information about the financial position of the business
5. Knowledge of profit and loss
Definition of Accounting
The process by which financial transactions are identified, entered, summarized and prepared by which the financial position of the business can be known is called accounting.
Business:-
Legal work done with the aim of earning profit is called business. Business is a broad term which includes trade, production work, buying and selling of goods or services, banks, insurance, transport companies.
Types of Business
- Manufacturing (उत्पादन)
- Trading (विक्रय)
- Servicing (सेवा)
Trade (व्यापार):-
Buying and selling of goods done with the aim of earning profit is called business.
Profession (पेशा या वृत्ति):-
Any work or means done to earn income which requires prior training is called profession, like the work of doctor, teacher, lawyer etc. comes under profession.
Proprietor (स्वामी या मालिक):-
The person starting a business who arranges the necessary capital and is entitled to profit and bears the risk of loss is called the owner of the business.
Capital (पूॅजी)-
The money invested by the business owner in the form of cash or other assets to start the business is called capital. Capital is invested in business for the purpose of earning profit. That part of the profit which is not withdrawn from the business,
Capital:- Assets – Liabilities.
Drawing (आहरण)–
The goods or cash which are withdrawn by the business owner for personal use of the business are called withdrawal or personal expenditure. Withdrawal reduces the amount of capital.
Transaction (सौदा या लेन – देन):–
Mutual exchange of money, goods or services between two parties is called business transaction. Economic activities like buying and selling of goods, giving and taking of payments etc. are called business deals or transactions.
Types of Transaction
- Cash Transaction (नगदलेन-देन)
- Credit Transaction (उधार या साखलेन-देन)
- Bill Transaction (बिललेन-देन)
Goods (माल) -
Goods are those items which are bought, sold or traded. Goods may include raw material, semi-manufactured material or finished goods obtained for the manufacture of goods.
Purchase (क्रय) -
When goods are purchased by a trader for sale, it is called purchase. This purchase can be in the form of raw material or finished goods. Purchase of assets is not included in purchase, because these are not for resale.
Purchase Return (क्रय वापसी) -
The goods which are returned due to any reason from the purchased goods are called purchase return or return outward.
Sales (विक्रय) -
When the purchased goods are sold for the purpose of earning profit, it is called sale. Selling goods for cash is called cash sale and selling goods on credit is called credit sale.
Sales Return (विक्रय वापसी) -
If the goods sold are returned by the customer due to any reason, it is called sales return or internal return. In Tally, when there is a Sales Return, it is entered in the Journal Voucher or Debit Note.
Stock (स्टाॅक या स्कंध) -
The goods which remain unsold after a certain period of time are called stock. The unsold goods on the last day of a business year are called closing stock. At the beginning of a new business year, this stock is called opening stock.
Assets (सम्पत्तियां)–
All such permanent and temporary items of the business which are necessary to run the business and which are owned by the businessman are called assets. Such as – machinery, land, building and all the machinery, furniture, printer, computer etc. used for personal use of the business.
Types of Assets
1. Fixed Assets (स्थायी सम्पत्ति)–
Machinery, land and all the machinery, furniture, printer, computer etc. used for personal use of the business.
2. Current Assets (चल सम्पत्ति)–
Cash, Bank cash etc.
Liabilities (दायित्व या देयताए)–
The amount payable by a business is called liabilities. There are some essential amounts in a business, the responsibility of paying which lies on the business like – capital, bills payable, creditors, bank overdraft etc.
Revenue (राजस्व) :-
Revenue means the amount which is received regularly from the sale of goods or services. The amounts received from the day-to-day activities of the business like – rent, interest, commission, discount, dividend etc. are also called revenue.
Expenses (व्यय) :-
The cost incurred for the production or procurement of goods, items and services in a business is called expenses. Payments for the procurement of goods and services come under expenses. Wages, freight, rail carriage and salary paid on the distribution and sale of goods, rent, advertising, expenses, insurance etc. are also included in expenses. In short, the cost of increasing revenue is called expenses. Types of Expenses
1. Direct Expenses –
Payment for the receipt of goods and services – wages, freight, railway carriage and payment on delivery and sale of goods
2. Indirect Expenses –
Increase in revenue, salary, rent, advertising, expenses, insurance etc. Expenditure:- Expense is the amount which is paid to increase the profit-earning capacity of the business. The payment made for the acquisition or receipt of assets in the business is called expense.
Gain (लाभ):-
This is a type of monetary receipt, which is obtained as a result of business, for example, if goods worth Rs. 1,00,000 are sold for Rs. 1,50,000, then the receipt of Rs. 50,000 will be called profit. Basic Accounting Terms
Cost (लागत):-
The sum of all direct and indirect expenses incurred for the production or making it useful, including raw materials, services and loans used in the business and its operations, is called the cost of the item. Raw materials or assets are included in the item.
Discount (कटौती, बट्टा या छूट):-
The discount given by the trader to his customers is called a cut, discount or rebate. It is also called a gift. There are two types of discounts –
1. Trade Discount ( व्यापारिक बट्टा ):-
The discount given by the seller to his customers on the marked price i.e. list price of the goods while purchasing them is called trade discount. It is given with the objective of increasing the sale of goods. It is not recorded in the books.
2. Cash Discount ( नगद बट्टा ):-
The discount given on payment of price in cash or by cheque within a fixed or stipulated period is called cash discount. It is recorded in the books.
Debitor (देनदार या ऋणी) :-
The person, firm or institution who borrows goods or services from another person is called trade debtor. Debtors are called ‘sundry debtors’.
Creditor (लेनदार या ऋण दाता) :-
The person, firm or institution from whom goods or services are taken on credit is called lender or creditor. Creditors emerge only when goods are purchased on credit. The creditors are called 'Sundry Creditors'. For example - 2 printers were purchased from Lakhan Shyam for Rs. 20000.
Receivable (प्राप्य) :-
The amount related to the business which is to be received is called receivable. In business, when goods are sold on credit, the buyer is called debtor, from whom the amount is to be received.
Payables ( देयतायें )-
There are some amounts in business which have to be paid by the businessman in future, they are called liabilities. Those from whom goods are purchased on credit by the business are called creditors of the business.
Entry:-
Writing the transaction in the accounting books is called entry.
Turn Over -
The sum of cash and credit sales in a given period is called total sales or turn over. Sales in cash + sales on credit = Turn Over.
Insolvent:-
A person who is unable to repay his debt is called bankrupt. The liability of such a person is more than the value of his property. In such a situation, he cannot repay his debt in full. He has to seek refuge in the court to repay the loan partially. The court declares him bankrupt and allows him to repay the loan partially, thereby freeing him from his debt.
Bad Debts:-
The amount which cannot be recovered due to the inability of the debtor or his becoming insolvent is called bad debt or irrecoverable debt for the creditor.
Debit and Credit:-
Every account has two sides. The left side is called debit or debit and the right side is called credit or calculation. Recording on the left side of an account is called debit account which is traditionally written as Dr. Similarly, recording on the right side of an account is called credit account which is traditionally written as Cr. It is worth mentioning that in the Indian book-keeping system, the debit side is on the right side and the credit is on the left side.
Commission:-
The remuneration given to a representative or agent in return for helping or representing in business activities is called commission.
Firm:-
In general sense, firm means an institution which does business or commercial work by establishing partnership, but in a broad sense, every business unit can be addressed as a firm.
Account / Leger:-
Ledger or account is a table in which the transactions are classified according to their nature and are written in sequence at one place under a heading. In simple words, the list made by sorting out the accounts related to a person, property and income-expenditure etc. is called Account / Leger.
The abbreviated form of the word Account in English is A/c. This abbreviated form is usually used in accounts and every account is divided into two sides. The left side is called Debit and the right side is called Credit.
Tally Ledger & Group
Elements |
Groups |
Balance |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Income |
Cr. |
|
Current Liability |
Dr. |
|
Bank Overdraft |
Cr. |
|
Bank Account |
Dr. |
|
Current Assets |
Dr. |
|
Fixed Assets |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Fixed Assets |
Dr. |
|
Liability (Loan) |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Fixed Assets |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Income |
Cr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Capital account |
Cr. |
|
Cash-in-hand |
Dr. |
|
Bank Account |
Dr. |
|
Cash account |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Income |
Cr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Dr. |
|
Capital account |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Income |
Cr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Cr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Dr. |
|
Fixed Assets |
Dr. |
|
Fixed Assets |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Dr. |
|
Goodwill |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expense |
Cr. |
|
Investment |
Dr. |
|
Indirect expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect expenses |
Dr. |
|
Fixed Assets |
Dr. |
|
Indirect expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect expenses |
Cr. |
|
Indirect expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect expenses |
Dr. |
|
Liability (loan) |
Cr. |
|
Indirect Income |
Cr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect expenses |
Dr. |
|
Current liability |
Cr. |
|
Current Assets |
Cr. |
|
Purchase account |
Dr. |
|
Purchase account |
Cr. |
|
Indirect expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect expenses |
Dr. |
|
Fixed Assets |
Dr. |
|
Fixed Assets |
Dr. |
|
Current Assets |
Dr. |
|
Current Liabilities |
Cr. |
|
Indirect expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect expenses |
Cr. |
|
Liability (loan) |
Cr. |
|
Loan & mortgage. |
Dr. |
|
Sales Account |
Dr. |
|
Purchase account |
Cr. |
|
Direct expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Income |
Cr. |
|
Reserve & Surpluses |
Cr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Sale account |
Cr. |
|
Sale account |
Dr. |
|
Sundry Creditors |
Cr. |
|
Sundry Debtors |
Dr. |
|
Stock-in-hand |
Dr. |
|
Fixed Assets |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Fixed Assets |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Purchase account |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Current Assets |
Dr. |
|
Fixed Assets |
Dr. |
|
Fixed Assets |
Dr. |
|
Fixed Assets |
Dr. |
|
Capital account |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Income |
Cr. |
|
Capital account |
Dr. |
|
Direct Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Current Assets |
Dr. |
|
Current Liability |
Cr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |
|
Indirect Expenses |
Dr. |